how to make a design 3d in illustrator
- Illustrator User Guide
- Get to know Illustrator
- Introduction to Illustrator
- What's new in Illustrator
- Common questions
- Illustrator system requirements
- Illustrator for Apple silicon
- Workspace
- Workspace basics
- Create documents
- Tools
- Customize keyboard shortcuts
- Artboards
- Customize the workspace
- Properties panel
- Set preferences
- Touch Workspace
- Microsoft Surface Dial support in Illustrator
- Recovery, undo, and automation
- Rotate view
- Rulers, grids, and guides
- Accessibility in Illustrator
- Safe Mode
- View artwork
- Use the Touch Bar with Illustrator
- Files and templates
- Synchronize settings using Adobe Creative Cloud
- Tools in Illustrator
- Selection
- Overview
- Selection
- Direct Selection
- Lasso
- Artboard
- Overview
- Navigation
- Overview
- Zoom
- Rotate View
- Paint
- Overview
- Gradient
- Shape Builder
- Type
- Overview
- Type
- Type on Path
- Selection
- Introduction to Illustrator
- Illustrator on the iPad
- Introduction to Illustrator on the iPad
- Illustrator on the iPad overview
- Illustrator on the iPad FAQs
- System requirements | Illustrator on the iPad
- What you can or cannot do on Illustrator on the iPad
- Workspace
- Illustrator on the iPad workspace
- Touch shortcuts and gestures
- Keyboard shortcuts for Illustrator on the iPad
- Manage your app settings
- Documents
- Work with documents in Illustrator on the iPad
- Import Photoshop and Fresco documents
- Select and arrange objects
- Create repeat objects
- Blend objects
- Drawing
- Draw and edit paths
- Draw and edit shapes
- Type
- Work with type and fonts
- Create text designs along a path
- Add your own fonts
- Work with images
- Vectorize raster images
- Color
- Apply colors and gradients
- Introduction to Illustrator on the iPad
- Cloud documents
- Basics
- Work with Illustrator cloud documents
- Share and collaborate on Illustrator cloud documents
- Upgrade cloud storage for Adobe Illustrator
- Illustrator cloud documents | Common questions
- Troubleshooting
- Troubleshoot create or save issues for Illustrator cloud documents
- Troubleshoot Illustrator cloud documents issues
- Basics
- Add and edit content
- Drawing
- Drawing basics
- Edit paths
- Draw pixel-perfect art
- Draw with the Pen, Curvature, or Pencil tool
- Draw simple lines and shapes
- Image Trace
- Simplify a path
- Define perspective grids
- Symbolism tools and symbol sets
- Adjust path segments
- Design a flower in 5 easy steps
- Perspective drawing
- Symbols
- Draw pixel-aligned paths for web workflows
- 3D effects and Adobe Substance materials
- About 3D effects in Illustrator
- Create 3D graphics
- Create 3D objects
- Create 3D Text
- About 3D effects in Illustrator
- Color
- About color
- Select colors
- Use and create swatches
- Adjust colors
- Use the Adobe Color Themes panel
- Color groups (harmonies)
- Color Themes panel
- Recolor your artwork
- Painting
- About painting
- Paint with fills and strokes
- Live Paint groups
- Gradients
- Brushes
- Transparency and blending modes
- Apply stroke on an object
- Create and edit patterns
- Meshes
- Patterns
- Select and arrange objects
- Select objects
- Layers
- Group and expand objects
- Move, align, and distribute objects
- Stack objects
- Lock, hide, and delete objects
- Duplicate objects
- Rotate and reflect objects
- Reshape objects
- Crop images
- Transform objects
- Combine objects
- Cut, divide, and trim objects
- Puppet Warp
- Scale, shear, and distort objects
- Blend objects
- Reshape using envelopes
- Reshape objects with effects
- Build new shapes with Shaper and Shape Builder tools
- Work with Live Corners
- Enhanced reshape workflows with touch support
- Edit clipping masks
- Live shapes
- Create shapes using the Shape Builder tool
- Global editing
- Type
- Create text
- Fonts and typography
- Format type
- Import and export text
- Format paragraphs
- Special characters
- Create type on a path
- Character and paragraph styles
- Tabs
- Text and type
- Find missing fonts (Typekit workflow)
- Update text from Illustrator 10
- Arabic and Hebrew type
- Fonts | FAQ and troubleshooting tips
- Create 3D text effect
- Creative typography designs
- Scale and rotate type
- Line and character spacing
- Hyphenation and line breaks
- Text enhancements
- Spelling and language dictionaries
- Format Asian characters
- Composers for Asian scripts
- Create text designs with blend objects
- Create a text poster using Image Trace
- Create special effects
- Work with effects
- Graphic styles
- Create a drop shadow
- Appearance attributes
- Create sketches and mosaics
- Drop shadows, glows, and feathering
- Summary of effects
- Web graphics
- Best practices for creating web graphics
- Graphs
- SVG
- Create animations
- Slices and image maps
- Drawing
- Import, export, and save
- Import
- Import artwork files
- Import bitmap images
- Import artwork from Photoshop
- Place multiple files | Illustrator CC
- Unembed images
- Import Adobe PDF files
- Import EPS, DCS, and AutoCAD files
- Links information
- Creative Cloud Libraries in Illustrator
- Creative Cloud Libraries in Illustrator
- Save
- Save artwork
- Export
- Use Illustrator artwork in Photoshop
- Export artwork
- Collect assets and export in batches
- Package files
- Create Adobe PDF files
- Extract CSS | Illustrator CC
- Adobe PDF options
- File information and metadata
- Import
- Printing
- Prepare for printing
- Set up documents for printing
- Change the page size and orientation
- Specify crop marks for trimming or aligning
- Get started with large canvas
- Printing
- Overprint
- Print with color management
- PostScript printing
- Print presets
- Printer's marks and bleeds
- Print and save transparent artwork
- Trapping
- Print color separations
- Print gradients, meshes, and color blends
- White Overprint
- Prepare for printing
- Automate tasks
- Data merge using the Variables panel
- Automation with scripts
- Automation with actions
- Troubleshooting
- Crash issues
- Recover files after crash
- File issues
- GPU device driver issues
- Wacom device issues
- DLL file issues
- Memory issues
- Preferences file issues
- Font issues
- Printer issues
- Share crash report with Adobe
3D tools are independent of the Perspective Grid tools and 3D objects are treated like any other object in perspective.
Create 3D objects
3D effects enable you to create three-dimensional (3D) objects from two-dimensional (2D) artwork. You can control the appearance of 3D objects with lighting, shading, rotation, and other properties. You can also map artwork onto each surface of a 3D object.
There are two ways to create a 3D object: by extruding or revolving. In addition, you can also rotate a 2D or 3D object in three dimensions. To apply or modify 3D effects for an existing 3D object, select the object and then double-click the effect in the Appearance panel.
3D objects may display anti-aliasing artifacts on screen, but these artifacts won't print or appear in artwork optimized for the web.
For a video about working with 3D objects in Illustrator, see Moving into the world of 3D.
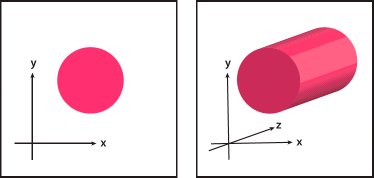
Create a 3D object by extruding
Extruding extends a 2D object along the object's z axis to add depth to the object. For example, if you extrude a 2D ellipse, it becomes a cylinder.
The object's axis always lies perpendicular to the object's front surface and moves relative to the object if the object is rotated in the 3D Options dialog box.
-
Click Effect > 3D(Classic) > Extrude & Bevel (Classic).
-
Click More Options to view the complete list of options, or Fewer Options to hide the extra options.
-
Select Preview to preview the effect in the document window.
-
Position
Sets how the object is rotated and the perspective from which you view it. (See Set 3D rotation position options.)
Extrude & Bevel
Determines the object's depth and the extent of any bevel added to or cut from it. (See Extrude & Bevel options.)
Surface
Creates a wide variety of surfaces, from dull and unshaded matte surfaces to glossy and highlighted surfaces that look like plastic. (See Surface shading options.)
Lighting
Adds one or more lights, varies the light intensity, changes the object's shading color, and moves lights around the object, for dramatic effects. (See Lighting options.)
Map
Maps artwork onto the surfaces of a 3D object. (See Map artwork to a 3D object.)
-

Extruded object without a beveled edge (left) compared to object with Bevel Extent In (middle) and with Bevel Extent Out (right)
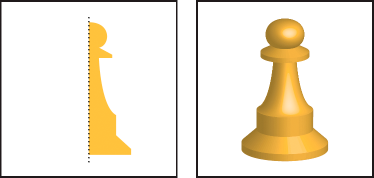
Create a 3D object by revolving
Revolving sweeps a path or profile in a circular direction around the global y axis (revolve axis) to create a 3D object. Because the revolve axis is vertically fixed, the open or closed path that you revolve typically needs to depict half of the desired 3D object's profile in a vertical and front-facing position; you can then rotate the 3D object's position in the effect's dialog box.
-
Applying the 3D Revolve effect to one or more objects simultaneously revolves each object around its own axis. Each object resides in its own 3D space and can't intersect other 3D objects. Applying the Revolve effect to a targeted group or layer, on the other hand, revolves the objects around a single axis.
Revolving a filled path with no stroke is much faster than revolving a stroked path.
-
Click Effect > 3D(Classic) > Revolve (Classic).
-
Select Preview to preview the effect in the document window.
-
Click More Options to view the complete list of options, or Fewer Options to hide the extra options.
Position
Sets how the object is rotated and the perspective from which you view it. (See Set 3D rotation position options.)
Revolve
Determines how to sweep the path around the object to turn it into three dimensions. (See Revolve options.)
Surface
Creates a wide variety of surfaces, from dull and unshaded matte surfaces to glossy and highlighted surfaces that look like plastic. (See Surface shading options.)
Lighting
Adds one or more lights, varies the light intensity, changes the object's shading color, and moves lights around the object, for dramatic effects. (See Lighting options.)
Map
Maps artwork onto the surfaces of a 3D object. (See Map artwork to a 3D object.)
Set options
Set 3D rotation position options
-
-
Select a preset position from the Position menu.
-
For unconstrained rotation, drag a track cube face. The front of the object is represented by the track cube's blue face, the object's top and bottom faces are light gray, the sides are medium gray, and the back face is dark gray.
-
To constrain the rotation along a global axis, hold down Shift while dragging horizontally (global y axis) or vertically (global x axis). To rotate the object around the global z axis, drag in the blue band that surrounds the track cube.
-
To constrain the rotation around an object axis, drag an edge on the track cube. The pointer changes to a double-sided arrow
 , and the cube edge changes color to identify the axis around which the object will rotate. Red edges represent the object's x axis, green edges represent the object's y axis, and blue edges represent the object's z axis.
, and the cube edge changes color to identify the axis around which the object will rotate. Red edges represent the object's x axis, green edges represent the object's y axis, and blue edges represent the object's z axis. -
Enter values between –180 and 180 in the horizontal (x) axis
 , vertical (y) axis
, vertical (y) axis , and depth (z) axis
, and depth (z) axis text boxes.
text boxes. -
To adjust the perspective, enter a value between 0 and 160 in the Perspective text box. A smaller angle is similar to a telephoto camera lens; a larger lens angle is similar to a wide-angle camera lens.
-
A lens angle that is higher than 150 may result in objects extending beyond your point of view and appearing distorted. Also, keep in mind that there are object x, y, and z axes and global x, y, and z axes. Object axes remain relative to an object's position in its 3D space. Global axes remain fixed relative to the computer screen; the x axis lies horizontally, the y axis lies vertically, and the z axis lies perpendicular to the computer screen.
Extrude & Bevel options
Extrude Depth
Sets the depth of the object, using a value between 0 and 2000.
Cap
Specifies whether the object appears solid (Revolve Cap On![]() ) or hollow (Revolve Cap Off
) or hollow (Revolve Cap Off![]() ).
).
Bevel
Applies the type of beveled edge you choose along the depth (z axis) of the object.
Height
Sets the height between 1 and 100. Bevel heights that are too large for an object may cause the object to self-intersect and produce unexpected results.
Bevel Extent Out
![]()
Adds the bevel to the object's original shape.
Bevel Extent In
![]()
Carves the bevel out of the object's original shape.
Revolve options
Angle
Sets the number of degrees to revolve the path, between 0 and 360.
Cap
Specifies whether the object appears solid (Revolve Cap On![]() ) or hollow (Revolve Cap Off
) or hollow (Revolve Cap Off![]() ).
).
Offset
Adds distance between the revolve axis and the path, to create a ring-shaped object, for instance. You can enter a value between 0 and 1000.
From
Sets the axis around which the object revolves, either the Left Edge or Right Edge.
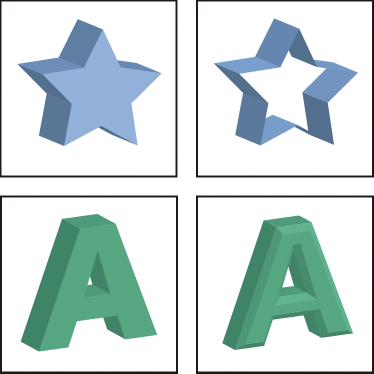
Surface shading options
Surface
Lets you choose options for the shading surfaces:
Wireframe
Outlines the contours of the object's geometry and makes each surface transparent.
No Shading
Adds no new surface properties to the object. The 3D object has the same color as the original 2D object.
Diffuse Shading
Makes the object reflect light in a soft, diffuse pattern.
Plastic Shading
Makes the object reflect light as if it were made of a shiny, high-gloss material.
note: Depending on what option you choose, different lighting options are available. If the object only uses the 3D Rotate effect, the only Surface choices available are Diffuse Shading or No Shading.
Light Intensity
Controls the light intensity between 0% and 100%.
Ambient Light
Controls the global lighting, which changes the brightness of all the object's surfaces uniformly. Enter a value between 0% and 100%.
Highlight Intensity
Controls how much the object reflects light, with values ranging from 0% to 100%. Lower values produce a matte surface, and higher values create a shinier-looking surface.
Highlight Size
Controls the size of the highlight from large (100%) to small (0%).
Blend Steps
Controls how smoothly the shading appears across the object's surfaces. Enter a value between 1 and 256. Higher numbers produce smoother shades and more paths than lower numbers.
Draw Hidden Faces
Displays the object's hidden backfaces. The backfaces are visible if the object is transparent, or if the object is expanded and then pulled apart.
Note: If your object has transparency and you want the hidden backfaces to display through the transparent front faces, apply the Object > Group command to the object before you apply the 3D effect.
Preserve Spot Color (Extrude & Bevel effect, Revolve effect, and Rotate effect)
Lets you preserve spot colors in the object. Spot colors can't be preserved if you chose Custom for the Shading Color option.
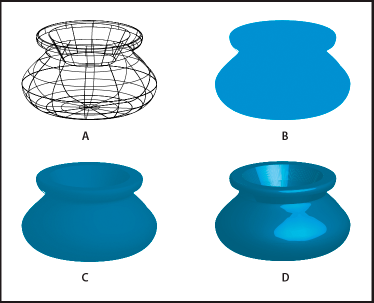
A. WireframeB. No shadingC. Diffuse shadingD. Plastic shading
Lighting options
Light
![]()
Defines where the light is. Drag the light to where you want it on the sphere.
Move Light Back button
![]()
Moves the selected light behind the object.
Move Light Front button
![]()
Moves the selected light in front of the object.
New Light button
![]()
Adds a light. By default, new lights appear in the front center of the sphere.
Delete Light button
Deletes the selected light.
note: By default, 3D Effects assigns one light to an object. You can add and delete lights, but the object must always have at least one light.
Light Intensity
Changes the selected light's intensity between 0% and 100%.
Shading Color
Controls the object's shading color, depending on the command you choose:
None
Adds no color to the shading.
Custom
Lets you choose a custom color. If you choose this option, click the Shade Color box to select a color in the Color Picker. Spot colors are changed to process colors.
Black Overprint
Avoids process colors if you're using a spot color workflow. The object is shaded by overprinting shades of black on top of the object's fill color. To view the shading, choose View >Overprint Preview.
Preserve Spot Color
Lets you preserve spot colors in the object. Spot colors can't be preserved if you chose Custom for the Shading Color option.
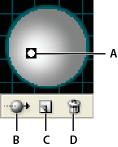
A. Selected light in frontB. Move selected light to back or front buttonC. New light buttonD. Delete light button
Add a custom bevel path
-
Open the Bevels.ai file, which is located in the Adobe Illustrator [version]\Support Files\Required\Resources\en_US\ folder (Windows) or Adobe Illustrator [version]\Required\Resources\en_US folder ((Mac OS).
-
Create a single open path in the Bevels.ai file.
-
Choose Window > Symbols, and do one of the following to make the path a symbol:
-
Drag the path to the Symbols panel.
-
With the path selected, click the New Symbol button
 in the Symbols panel or click New Symbol from the panel menu.
in the Symbols panel or click New Symbol from the panel menu.
-
-
To rename the symbol, double-click the symbol in the Symbols panel, enter a name in the Symbol Options dialog box, and clickOK.
-
ClickFile > Save. If the Save option doesn't work, clickFile > Save As to save the file as a local copy to the computer. Rename the file and move it back to the original location: Adobe Illustrator [version]\Support Files\Required\Resources\en_US\ folder (Windows) or Adobe Illustrator [version]\Required\Resources\en_US folder ((Mac OS). The existing file in the original destination is replaced.
-
Quit Illustrator and relaunch the application.
The Bevel menu in the 3D Extrude & Bevel Options dialog box lists the bevel.
-
To apply the custom bevel, do one of the following:
-
To apply the bevel to an extruded 3D object, select the 3D object, and double-click the 3D Extrude & Bevel effect in the Appearance panel. In the 3D Extrude & Bevel Options dialog box, choose the bevel from the Bevel menu.
-
To apply the custom bevel to 2D artwork, select the 2D object, and choose Effect > 3D > Extrude & Bevel. In the 3D Extrude & Bevel Options dialog box, choose the custom bevel from the Bevel menu.
-
Rotate an object in three dimensions
-
Choose Effect > 3D(Classic) > Rotate (Classic).
-
Select Preview to preview the effect in the document window.
-
Click More Options to view the complete list of options, or Fewer Options to hide the extra options.
-
Position
Sets how the object is rotated and the perspective from which you view it. (See Set 3D rotation position options.)
Surface
Creates a wide variety of surfaces, from dull and unshaded matte surfaces to glossy and highlighted surfaces that look like plastic. (See Surface shading options.)
Map artwork to a 3D object
Every 3D object is composed of multiple surfaces. For example, an extruded square becomes a cube that is made of six surfaces: the front and back faces, and the four side faces. You can map 2D artwork to each surface on a 3D object. For example, you might want to map a label or text onto a bottle-shaped object or simply add different textures to each side of an object.
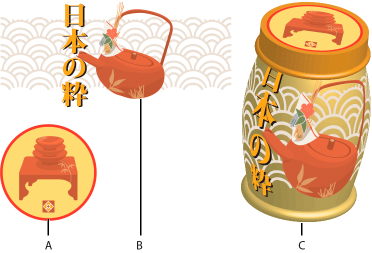
A. Symbol artworkB. Symbol artworkC. A and B mapped to 3D object
You can only map 2D artwork that's stored in the Symbols panel to a 3D object. Symbols can be any Illustrator art object, including paths, compound paths, text, raster images, mesh objects, and groups of objects.
When mapping 3D objects, consider the following:
-
Because the Map Art feature uses symbols for mapping, you can edit a symbol instance and then automatically update all surfaces that are mapped with it.
-
You can interact with the symbol in the Map Art dialog box with normal bounding box controls to move, scale, or rotate the object.
-
The 3D effect remembers each mapped surface on an object as a number. If you edit the 3D object or apply the same effect to a new object, there may be fewer or more sides than the original. If there are fewer surfaces than the number of surfaces defined for the original mapping, the extra artwork will be ignored.
-
Because a symbol's position is relative to the center of an object surface, if the geometry of the surface changes, then the symbol will be remapped relative to the new center of the object.
-
You can map artwork to objects that use the Extrude & Bevel or Revolve effect, but you can't map artwork to objects that only use the Rotate effect.
-
In the Appearance panel, double-click the 3D Extrude & Bevel or 3D Revolve effect.
-
Choose the artwork to map to the selected surface from the Symbol pop‑up menu.
-
A light gray color mark appears on the surfaces that are currently visible. A dark gray color mark appears on the surfaces that are hidden by the object's current position. When a surface is selected in the dialog box, the selected surface is outlined in red in the document window.
-
-
To move the symbol, position the pointer inside the bounding box and drag; to scale, drag a side or corner handle; to rotate, drag outside and near a bounding box handle.
-
To make the mapped artwork fit to the boundaries of the selected surface, click Scale To Fit.
-
To remove artwork from a single surface, select the surface using the Surface options, and then either clickNone from the Symbol menu or click Clear.
-
To remove all maps from all of the 3D object's surfaces, click Clear All.
-
To shade and apply the object's lighting to the mapped artwork, select Shade Artwork.
-
To show only the artwork map, not the geometry of a 3D object, select Invisible Geometry. This is useful when you want to use the 3D mapping feature as a three-dimensional warping tool. For example, you could use this option to map text to the side of an extruded wavy line, so that the text appears warped as if on a flag.
-
To preview the effect, select Preview.
-
-
ClickOK in the Map Artwork dialog box.
3D tools are independent of Illustrator's Perspective Grid tools. 3D objects are treated like any other art when placed in Perspective Grid.
how to make a design 3d in illustrator
Source: https://helpx.adobe.com/illustrator/using/creating-3d-objects.html